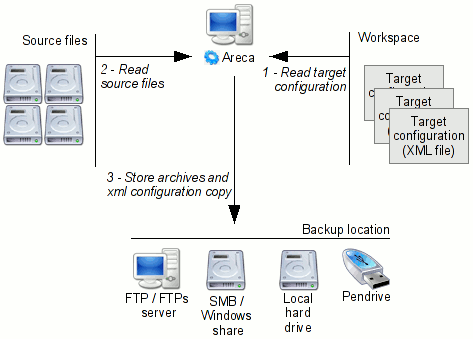
In today’s age where securing data is of utmost importance, it is crucial for organizations and individuals to become proficient in backup and remote wiping techniques. This article offers an insight into the complexities of managing data, with a special emphasis on protecting your digital resources and maintaining confidentiality under difficult circumstances.
Understanding Backup and Remote Wiping
In data management, backup and remote wiping procedures play two essential but separate roles. Backup entails making copies of computer data for archiving purposes to restore lost information later. On the other hand, remote wiping involves deleting sensitive device contents from a distance to prevent unauthorized access or theft of crucial information.
Backup
Creating duplicate copies of data through regular backups is essential in safeguarding the integrity of information and guaranteeing uninterrupted business operations. This practice helps organizations to reduce risks related to hardware malfunctions, cyber threats, unintentional deletions, as well as natural catastrophes.
- Data Recovery: Quickly recover lost or corrupted data
- Continuity: Promotes operational efficiency and minimizes downtime.
- Protection: Shields from ransomware as well as other forms of internet security risks.
- Compliance: Enables the fulfillment of regulatory obligations concerning data retention and accessibility.
Remote Wiping
In order to ensure the protection of sensitive information in cases where devices are lost, stolen or compromised, remote wiping is a crucial step. It enables organizations to erase data from a distance and avoid unauthorized access thereby maintaining privacy at all times.
- Immediate Response: Facilitates prompt measures to alleviate data breach hazards.
- Data Erasure: Ensures complete removal of data from the device.
- Compliance: Aligns with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
- Control: Facilitates centralized administration of security measures for devices.
When to Backup: Optimal Strategies for Data Security
To achieve better backup procedures, it is advised to align the timing and frequency of backups with data’s value and criticality. Here are some recommended practices for implementing secure backup operations:
Regularly Scheduled Backups
To reduce the chances of data loss, standard backups entail producing replicas of information at predetermined times. This method permits entities to retrieve data from different instances based on how often they back up their systems.
- Daily Backups: Daily backups ensure that any changes or updates to data are captured on a daily basis, enabling the recovery of recent snapshots in case of system failures or unintentional deletions.
- Weekly Backups: The weekly backups provide a thorough backup of the data from the week, which can be used to restore information in case of major incidents or system failures.
- Monthly Backups: Monthly backups offer a reliable backup solution that ensures data integrity for extended durations, while simultaneously providing the basis for historical records.
Real-Time Backup Solutions
Real-time backup solutions provide uninterrupted replication of modifications to a remote location for crucial information that demands immediate security. This approach guarantees minimal loss of data and rapid restoration in unforeseen disruptions.
- Immediate Data Capture: Data changes are automatically captured in real-time, ensuring that replication is up-to-date and reducing the possibility of inconsistent data.
- Offsite Storage: The backup copies are securely stored in offsite locations or cloud environments, safeguarding the primary storage systems from physical damage or onsite disasters.
- Data Accessibility: Facilitating quick retrieval of the latest data versions, enhances operational continuity and minimizes downtime in accessing information.
Remote Wiping Essentials: When and How to Wipe Data Remotely

Knowing the appropriate moment to carry out remote wiping is essential for upholding data security in situations where devices have been compromised.
Lost or Stolen Devices
To prevent potential data breaches and safeguard confidential information, prompt action becomes crucial in cases of lost or stolen devices.
- Immediate Response: Upon discovering a lost or stolen device, take immediate action by initiating remote wiping to prevent any unauthorized access and potential misuse of sensitive data.
- Comprehensive Data Erasure: Guarantee thorough elimination of all information, such as corporate emails, documents and stored credentials from the device via secure data erasure.
- Remote Management Tools: Effectively and securely execute the wipe command through either remote management solutions or Mobile Device Management (MDM) platforms.
Employee Departure
If employees utilize their personal devices for work-related tasks and leave the company, remote wiping is crucial to protect corporate data and maintain adherence to data security regulations.
- Policy Enforcement: The implementation and enforcement of policies that require erasure of company data from personal devices upon an employee’s departure or termination.
- Data Protection Measures: To prevent unauthorized access and potential data breaches of sensitive information, all corporate data must be wiped out from the device.
- Documentation and Compliance: To ensure adherence to data protection regulations such as GDPR, CCPA and industry-specific standards, it is important to maintain comprehensive records of all remote wipe actions taken
Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Backup Procedures
Follow these detailed steps to establish a robust backup system for maintaining data integrity:
Choose Your Backup Medium
The first crucial stage in setting up a dependable backup system is choosing the suitable backup media. Evaluate these alternatives according to your company’s requirements and amount of data:
- External Drives: Consider using portable or external hard drives as a cost-effective local backup solution. It’s important to choose high-capacity and reliable drives for storage purposes. Additionally, regularly rotating these drives can minimize the risk of potential data loss caused by hardware failure or physical damage.
- Cloud Storage: For secure offsite storage and access from anywhere, consider cloud-based backup solutions. It’s important to select reliable providers who offer strong security measures such as data encryption, compliance certifications (e.g., ISO 27001, SOC 2), and other essential features like ample storage capacity or scalability options. Be sure to also evaluate the recovery capabilities of your chosen cloud service provider before committing long-term.
- Dedicated Backup Servers: To ensure centralized data storage and management, consider deploying dedicated backup servers in your network infrastructure. These specialized servers allow for greater control over backup policies, access management, and data retention. To prevent hardware failures and maintain uninterrupted availability of critical information, these servers should feature redundancy features like RAID configurations or backup replication capabilities.
Set Up Automated Backups
To achieve consistent data protection without the intervention of humans and to avoid errors, it is essential to automate the backup process. To effectively implement automated backups, follow these steps:
- Choose Backup Software: Opt for a reliable choice that incorporates scheduling, encryption and compression features. Examples of well-known options are Acronis True Image, Veeam Backup & Replication and Backup Exec. Confirm the product’s compatibility with your present IT infrastructure as well as operating systems before making any decisions regarding it.
- Configure Backup Schedule: Establish backup schedules according to the significance of data and operational necessities. Plan backups on a daily, weekly or monthly basis to ensure comprehensive recording of modifications and advancements. Tweak the frequency and timing in line with business hours, patterns of data usage as well as network bandwidth accessibility.
- Set Retention Policies: Develop retention policies that enable you to administer backup versions and enhance storage usage. Identify the duration of time for retaining duplicated backups according to data governance regulations, conformity requirements and operational retrieval objectives. Introduce lifecycle management procedures which will automatically save important information over longer periods while disposing off outdated backups appropriately .
Test Backup Recovery
To ensure the integrity of data and prepare for any potential loss or system failure, it is imperative to conduct routine tests on backup recovery procedures. Use these guidelines to confirm your ability to recover from a backup:
- Create Test Scenarios: Formulate all-embracing test scenarios that emulate prevalent occurrences of data loss, comprising but not limited to hardware malfunctions, inadvertent removals, ransomware assaults or acts of nature. Encompass situations that entail restoring both full and partial information in order to appraise the tenacity of backup systems.
- Execute Recovery Tests: Conduct planned recovery tests utilizing backup copies to confirm the accessibility, coherence and utility of data. Validate compliance with business continuity requirements of both the recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO). Record test findings with details on any challenges that may have arisen during the restoration process, ranking remedial steps in accordance to priority.
- Document Results and Improve Processes: Note the outcome of tests, such as recovery performance metrics, vulnerability identification results. Use test outcomes to perfect backup approaches, amend recovery protocols and improve data safeguarding measures. Work jointly with beneficiaries, IT staff members alongside officers in charge of securing data to execute corrective procedures while reducing possible threats effectively.
How to Perform a Remote Wipe: A Detailed Protocol

Careful consideration must be given when executing a remote wipe to ensure that all sensitive data is erased securely.
Select a Remote Wipe Software
When selecting remote wipe software, it is crucial to consider the following factors as they play a key role in implementing and securely managing remote wiping operations.
- Features: Select a software that is equipped with capabilities such as compliance to data protection regulations like HIPAA and GDPR, remote wipe commands, and data encryption.
- Compatibility: Ensure that your organization’s devices and operating systems, such as Windows, macOS, iOS and Android are compatible with one another.
- Security Measures: Assessment of security measures involves examining authentication protocols that are strong, encryption standards which are reliable and remote management capabilities that cover all aspects to deter unauthorized access.
- Reporting and Auditing: To ensure compliance and accountability, choose software that offers extensive reporting capabilities and preserves a record of remote wiping actions through audit trails in Reporting and Auditing tasks.
Configure Device Management Settings
To ensure proper configuration and enrollment in a centralized device management system, make sure to take the following steps for effective device management settings before initiating a remote wipe:
- Enrollment: Use a Mobile Device Management (MDM) platform or other device management tool that allows for remote wiping capabilities.
- Policy Implementation: Define and enforce policies within the device management console for remote wipe procedures. Specify conditions under which remote wipes can be initiated, such as device loss, theft, or security breaches.
- User Notifications: Clearly communicate remote wipe policies and procedures to users through user notifications.
- Backup Verification: Confirm that current backups are securely stored on devices for effective data retrieval in the event of a remote wipe.
Initiate the Remote Wipe
After finishing all preparations, carry out the remote wipe process in case of a security breach or loss notification. Ensure secure execution of the remote wipe command by adhering to these steps:
- Authentication: To prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data, it is crucial to authenticate both the identity and authorization of the individual initiating remote wipe.
- Remote Command Execution: To perform a secure remote wipe, either use the designated software for wiping remotely or employ the management console of the device.
- Confirmation and Monitoring: Receive confirmation of the remote wipe completion and monitor the process to ensure all data on the device is securely erased beyond recovery.
- Documentation: Document vital information regarding the remote wipe procedure. Such details should include execution date and time, device identification data as well as confirmation of successful erasure of applicable records.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Remote Wiping
To avoid any breach of privacy laws, the implementation of remote wiping procedures must be carried out in accordance with legal frameworks.
Consent
Before initiating any remote wiping actions, it is essential to obtain informed consent from device users. Some aspects that should be considered regarding obtaining consent are:
- Informed Consent: It is important to thoroughly educate device users about remote wipe policies, procedures and possible outcomes. This can be achieved by providing clear and concise explanations in user agreements, employment contracts or acceptable use policies outlining the circumstances under which remote wiping may take place.
- Transparency: Communicate remote wipe policies and procedures clearly. Specify the situations where initiating a remote wipe may be necessary such as in cases of device loss, theft or security breaches.
- Revocation of Consent: Provide mechanisms for users to revoke consent for remote wiping actions. Allow users the option to opt-out or withdraw their authorization if they do not wish to have their data remotely wiped.
Proportionality
Adhering to the principle of proportionality ensures that remote wiping is used appropriately and only as a last resort in specific circumstances. Consider the following guidelines for proportionate use:
- Risk Assessment: Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to evaluate the severity of potential harm or data breach before initiating a remote wipe. Assess factors such as the sensitivity of the data stored on the device and the likelihood of unauthorized access.
- Data Sensitivity: Prioritize remote wiping actions for devices containing highly sensitive or confidential information that could pose significant risks if accessed by unauthorized parties.
- Alternative Measures: Explore alternative data protection measures, such as encryption, remote lock, or data backup, before resorting to remote wiping. Determine if these measures can mitigate risks effectively without permanently deleting data.
Legal Frameworks and Compliance
Understanding and complying with applicable legal frameworks is crucial to avoid legal repercussions and maintain robust data protection standards:
- Data Protection Laws: Familiarize yourself with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and other regional or industry-specific laws. Ensure that remote wiping practices align with legal requirements regarding data privacy, security, and user rights.
- Cross-Border Considerations: Assess the legal implications of conducting remote wipes across international borders. Be mindful of differing privacy laws and jurisdictional requirements that may impact the legality and scope of remote wiping actions.
- Documentation and Audit Trails: Maintain meticulous documentation of remote wipe actions, including the rationale for initiation, authorization details, and confirmation of data erasure. Establish robust audit trails to demonstrate compliance with legal obligations during audits, regulatory inspections, or legal inquiries.
Ethical Considerations
In addition to legal obligations, ethical considerations play a pivotal role in shaping responsible remote wiping practices:
- Respect for Privacy: Uphold user privacy rights by minimizing data access and ensuring that remote wiping actions are proportionate to the risks posed by unauthorized access or data breaches.
- Accountability: Hold individuals accountable for initiating remote wiping actions. Establish clear roles and responsibilities within the organization to ensure adherence to remote wipe policies, legal requirements, and ethical standards.
- Trust and Transparency: Foster trust with device users through transparent communication about remote wipe procedures. Clearly communicate the purpose of remote wiping, the protective measures in place to safeguard data, and the rights of users regarding their personal information.
Future Trends in Backup and Remote Wiping Technologies

As technology evolves, so do the methods of backup and remote wiping. Future trends include:
Increased Automation
Automation is set to redefine backup and remote wiping processes, offering efficiency, reliability, and enhanced data protection capabilities. Key trends in automation include:
- Scheduled and Real-Time Backups: Future backup solutions will feature sophisticated scheduling mechanisms that automate backups at specified intervals (daily, weekly, monthly). Real-time backup technologies will continuously capture and replicate data changes, ensuring minimal data loss and faster recovery times in the event of a disruption.
- Automated Remote Wiping: Automation will extend to remote wiping procedures, allowing organizations to trigger wipes automatically based on predefined conditions such as device loss, theft, or detected security breaches. Automated remote wiping enhances response times, reduces human error, and ensures swift mitigation of data exposure risks.
Integration with AI
AI integration is transforming data security practices by enabling predictive analytics and proactive threat mitigation strategies. Future trends in AI integration include:
- Threat Prediction and Detection: AI algorithms will analyze vast datasets to detect patterns indicative of potential data breaches or security vulnerabilities. Machine learning models will predict threats before they materialize, enabling organizations to take preemptive actions such as initiating remote wipes to safeguard sensitive data.
- Behavioral Analysis: AI-driven behavioral analytics will monitor user and device behaviors in real-time, detecting anomalous activities that may signal unauthorized access or data misuse. By leveraging behavioral analysis, organizations can proactively respond to security incidents, including implementing remote wiping as a protective measure.
Advantages of Future Trends
Embracing these future trends in backup and remote wiping technologies offers numerous advantages for organizations:
- Enhanced Data Protection: Automation reduces the reliance on manual processes, minimizing human error and ensuring consistent adherence to backup and remote wiping policies. This enhances overall data protection and resilience against cyber threats.
- Operational Efficiency: Automated processes streamline data management tasks, freeing up IT resources to focus on strategic initiatives and innovation rather than routine maintenance activities.
- Proactive Security Measures: AI-powered predictive analytics enable proactive identification and mitigation of potential security risks, enhancing the organization’s ability to respond swiftly and effectively to emerging threats.
- Compliance Readiness: Automated logging and reporting capabilities facilitate comprehensive documentation of backup and remote wiping activities, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and simplifying audit processes.
Conclusion
By understanding and implementing effective backup and remote wiping procedures, individuals and organizations can protect themselves from data loss and security breaches, ensuring that their digital environments are resilient and secure.
FAQ
A: The frequency depends on the data’s importance. Critical data might require daily or real-time backups, while less critical data may be backed up weekly.
A: Remote wipes are designed to erase data permanently, but advanced forensic methods may sometimes recover fragments.
A: If not properly configured, remote wipes can lead to data loss or affect unintended devices.